What are the upcoming trends in the automotive industry?
Introduction: The automotive industry is on the verge of a transformation
In recent years, the automobile industry has undergone extraordinary transition, with new technologies such as electrification, autonomous driving, and smart connection changing the notion of a typical car. According to McKinsey & Company, a worldwide consulting organization, electric vehicles will account for more than 30% of global new car sales by 2030, far outpacing current market share. This movement is driven not only by technology breakthroughs, but also by worldwide governmental support and rising consumer environmental consciousness. For example, European countries and numerous states in the United States have adopted a ‘no-fuel’ policy and want to phase out the sale of fuel vehicles by 2035.So, how will the cars of the future look? More than merely a mode of transportation, the future car may resemble a’mobile intelligent terminal’, meeting more of our demands. The change in the automobile industry, from all-electric to autonomous driving to shared mobility, will provide more convenient and greener mobility to the world, as well as significant challenges and opportunities for traditional automotive manufacturing and services. Next, we’ll look in depth at some of the biggest trends in the industry now and how they will affect the future of mobility.
1. Trend One: Electrification

Electrification is becoming a key trend in the automotive industry, drawing the attention of nearly all major automakers. More and more brands are actively converting to electric (EV) or hybrid (HEV) vehicles. According to the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) 2023 study, global EV sales have doubled in the last five years, with EVs accounting for 14% of the global new car market in 2023 and predicted to rise to 50% over the next decade.
Better batteries and more charge sites have contributed to the growing popularity of electric vehicles. Car and technology businesses are working on new electric vehicle technologies to increase range and safety. At the same time, governments are creating additional charging stations. The United States intends to have 500,000 by 2030, whereas China wishes to have more in order to accomplish ‘one kilometre charging’.
From an environmental standpoint, electric vehicles may dramatically reduce exhaust emissions and noise pollution, particularly in cities, and the improvement in air quality is especially noticeable. For example, British research indicates that pure electrification can reduce urban carbon dioxide emissions by 30% over the next 15 years, offering a greener living environment for metropolitan dwellers.
Looking ahead, electrification will revolutionize not only the car industry, but also the entire transport ecosystem. Strong regulatory support and market demand for environmentally friendly transportation have elevated electrification from a trend to a future mainstream. Electric vehicles will gain popularity as battery costs fall, power grid capacity improves, and quick charging technology matures.
2. Trend Two: Autonomous Driving
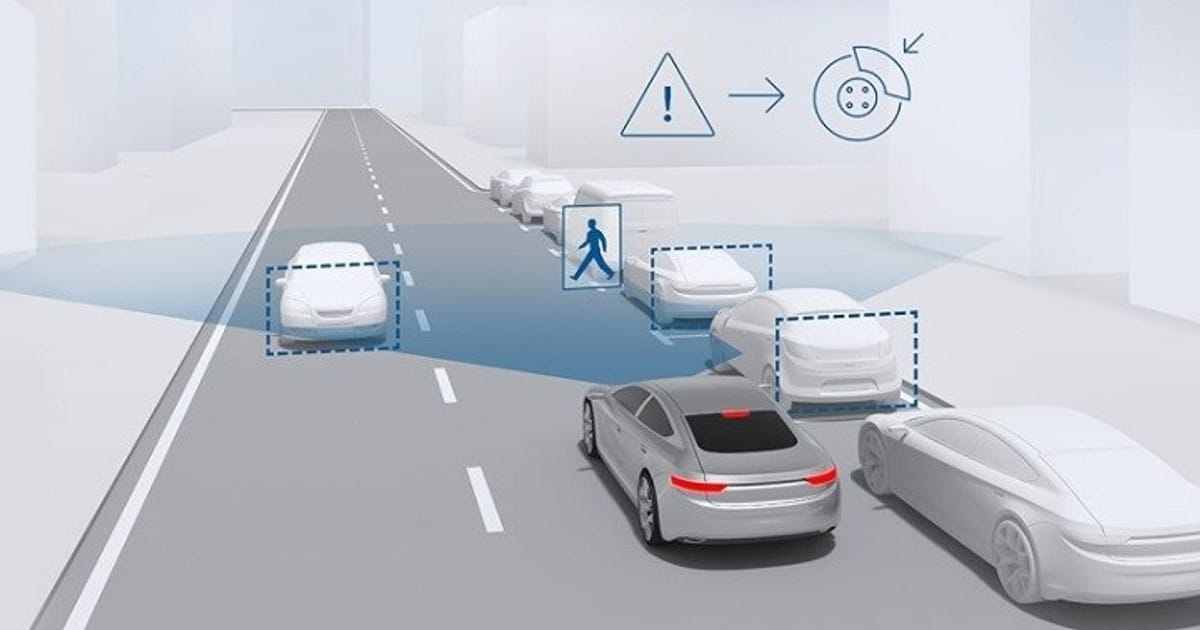
Autonomous driving technology is increasingly migrating from pilot to mass-production applications, with L2 and L3 degrees of autonomy becoming ubiquitous on many countries’ roadways.According to SAE (International Society of Automotive Engineering), L2 is ‘partially autonomous driving’, which means the car can accelerate, brake, and steer automatically, but the driver must be ready to take over. L3 stands for ‘conditional automatic driving,’ which allows the vehicle to drive completely autonomously under specific situations and requires the driver to take control only in an emergency. L3 is “conditional autonomous driving,” which can drive completely independently in certain scenarios. Many automakers, including Tesla, Mercedes-Benz, and BMW, have introduced L2 and L3 self-driving vehicles. In 2023, more than 5 million L2 and L3 self-driving cars will be sold worldwide.The most significant benefit of autonomous driving technology is increased driving safety, logistics, and transportation efficiency. According to data from the United States Department of Transportation, human error accounts for around 94% of traffic accidents, therefore the maturity of automatic driving technology is predicted to lower the frequency of accidents and increase overall road safety. Furthermore, autonomous driving has the potential to enhance transportation efficiency, lower labor costs, and cut fuel consumption, making long-distance logistics more cost-effective and ecologically benign. The promotion of self-driving trucks is particularly promising for unmanned high-speed transportation.From a future standpoint, L4 and beyond (i.e., ‘highly automated’ and ‘completely automated’) offer enormous potential, but they are still plagued by technical bottlenecks and regulatory obstacles.The realization of L4 and L5 needs the vehicle to be entirely automated in all conditions, with no reliance on human intervention. The realization of L4 and L5 needs the vehicle to be completely autonomous in any situation, without relying on human intervention, which necessitates more accurate sensors, faster information processing capabilities, and comprehensive real-time map coverage. Furthermore, traffic safety standards in various nations must be gradually changed to ensure that self-driving vehicles are legal and safe in a variety of conditions.As technology advances and the legal environment improves, the potential of self-driving cars becomes increasingly appealing. It will not only change our view of driving, but will also transform the logistics and urban transport patterns, providing humanity with a safer, more efficient, and environmentally friendly mode of transportation.
3. Trend Three: Smart Connected Vehicles

5G networks and new telematics technology are elevating intelligent connectivity to a new level in the automotive industry. The networking of future automobiles is becoming reality. Cars may access real-time information on other vehicles, road conditions, traffic signals, and other factors, allowing for better traffic management. According to McKinsey, by 2030, more than 70% of new automobiles will have 5G or greater, increasing the appeal of smart connection.The primary impact of smart connection is to increase driving safety, traffic efficiency, and the user experience. To begin, smart connectivity greatly reduces the number of traffic accidents, for example, by providing advance warning of impending situations using V2V technology, so avoiding collisions. Second, the interaction of smart vehicles with road infrastructure improves traffic flow and reduces congestion. According to studies, smart connection technology is predicted to improve urban traffic flow by more than 20%, effectively reducing traffic congestion in major cities. Finally, smart connectivity allows drivers to use more intuitive and personalized navigation services, as well as remote vehicle control, making travel more convenient.Intelligent networking will become standard in automobiles. Vehicles will be able to communicate with the smart city as technology advances and smart transportation becomes more widespread. This will lead to an improved transportation system. Intelligent networking will be critical for travel in the future.
4. Trend Four: Shared Mobility

Sharing modes in the travel sector are becoming more common as the sharing economy grows. Shared mobility alternatives, such as car-sharing, Internet car-sharing, shared electric motorcycles, and electric bicycles, make transportation more convenient and flexible. PricewaterhouseCoopers estimates that the worldwide shared mobility business will be worth hundreds of billions of dollars by 2030. Consumers, particularly in metropolitan areas, are becoming increasingly amenable to sharing modes, and many young people are no longer purchasing a car as their primary mode of transportation.
Shared mobility has had a good influence in several ways. First, it considerably lowers the need for individuals to possess automobiles, cutting vehicle density in cities and alleviating congestion. According to a McKinsey report, if shared mobility becomes mainstream, the number of cars in the world might be decreased by up to 10% per year, with huge implications for urban traffic. Furthermore, shared mobility is contributing to the trend of ‘car-free’ mobility, particularly in more densely populated places, where more individuals prefer flexible and economical shared mobility over private cars. This not only lowers greenhouse gas emissions, but also promotes more efficient road use and fewer traffic accidents.
As urbanisation accelerates, more cities will encourage the development of shared mobility infrastructure, such as more shared vehicle parking spaces and charging stations. Meanwhile, customers’ perceptions of car ownership are shifting, with an increasing number of individuals opting to utilize transportation on demand rather than owning one for an extended period. Shared mobility is no longer just for short-term convenience; it is gradually evolving into a new way of life, delivering more flexible and environmentally friendly alternatives to urban transportation.
5. Trend Five: Sustainability

Environmental protection and low carbon emissions have been the primary goals of the automotive industry’s development. More and more automakers are shifting to sustainable development, not just by innovating in electrification but also by optimizing raw material selection, manufacturing processes, and supply chain management. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the global transportation sector contributes for around 25% of total carbon emissions, placing a huge responsibility on the automotive industry to tackle climate change. To lower their carbon footprint, several firms have begun to employ renewable resources, optimize their manufacturing processes, and invest in environmentally friendly technologies.
The effect of sustainability on the sector is obvious. To begin, lowering carbon emissions and optimizing resource utilization are critical components of attaining environmental goals. Major worldwide automotive firms are actively encouraging green production, including the use of natural fibers and lightweight materials, which minimizes energy consumption throughout the car manufacturing process while simultaneously improving vehicle fuel efficiency. Tesla, for example, not only makes zero-emission electric vehicles, but it also uses solar panels and other renewable energy sources in its plants to achieve ‘zero emissions’ during the manufacturing process. Furthermore, consumers are more likely to favor brands that actively promote environmental and social sustainability.
As environmental regulations tighten and consumers become more environmentally conscious, automakers will be required not only to reduce carbon emissions from their vehicles, but also to make greater efforts in the areas of life-cycle management, recycling, and energy consumption. The car of the future will be more than just a low-emission green transportation tool; it will also be resource-efficient, recyclable, and environmentally beneficial. This transition will catalyze the entire sector toward a greener, more sustainable future.
6.The Importance of Automotive Training Equipment
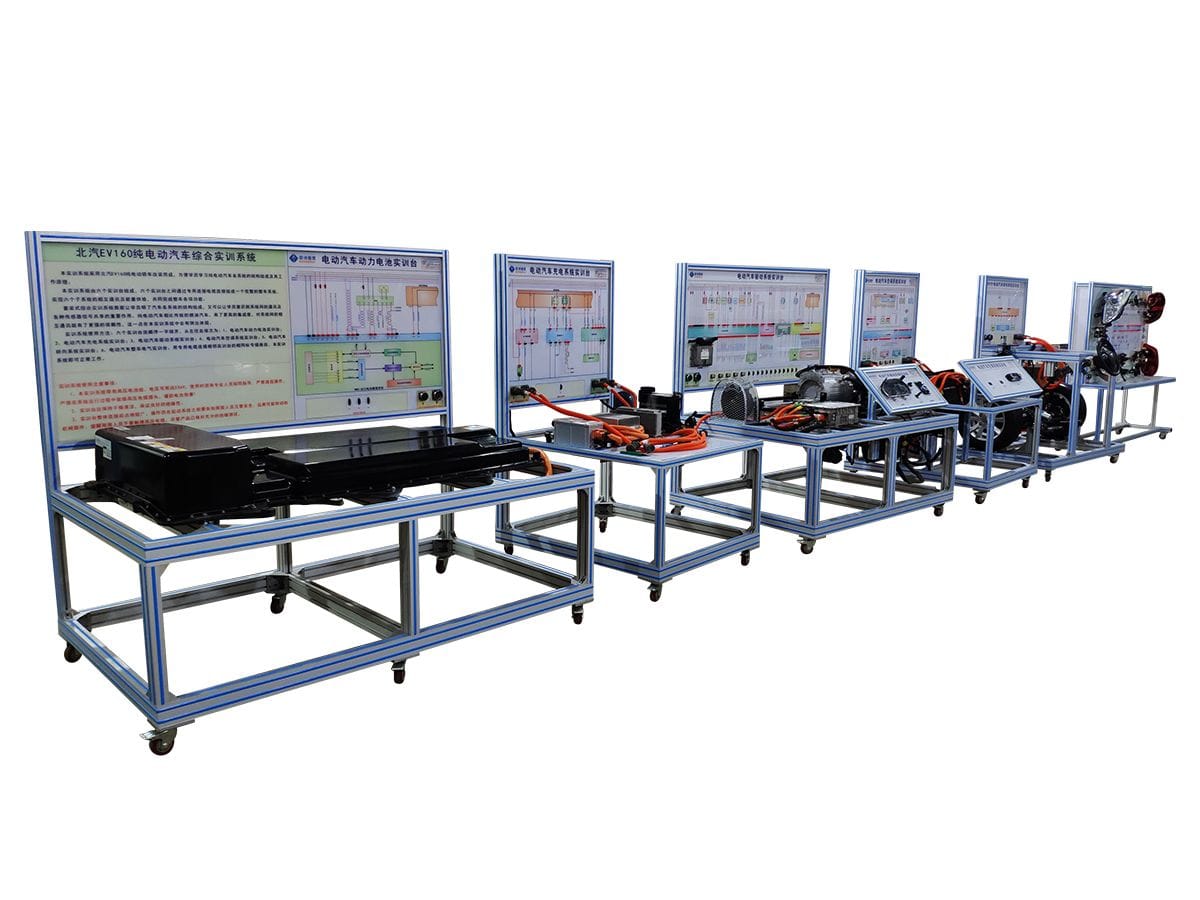

New technologies such as electric automobiles, self-driving cars, and the Internet of automobiles are transforming the auto sector. These technologies are rapidly evolving, as are the skills required for automobiles. Training must evolve with the times, particularly as there is an increasing demand for it. According to the worldwide Automotive Industry Report, by 2030, electric vehicles will account for around 30% of worldwide new car sales. This means that training in associated maintenance procedures will be in great demand, and training equipment will become increasingly necessary.
Automotive training equipment is essential. They assist trainees in learning about new technologies and mastering electric car charging technology, self-driving control systems, and Telematics network operations. Trainees learn by doing. They improve their theoretical knowledge by modeling real-world driving conditions and system operations. This ensures that future automotive technologists can adjust to industry changes. For example, during autonomous driving training, learners are exposed to a variety of driving scenarios and emergency circumstances.
For more detailed information on automotive training equipment, visit our website(https://gdzcee.com/) to explore more solutions for the future of automotive technology training.
7. Conclusion: Seizing Opportunities in Future Trends
With trends like electrification, autonomous driving, connectivity, shared mobility, and sustainability driving the transformation of the automotive industry, the sector is moving towards a more intelligent and environmentally friendly future. These changes are impacting not only vehicle manufacturing and usage but also raising new demands for maintenance and technical training. According to McKinsey, by 2030, technological shifts in the global automotive industry will create more than $2 trillion in market opportunities.
As these trends accelerate, the industry increasingly needs advanced equipment and skilled professionals to master these new technologies. Training is especially critical in areas like electric vehicles, autonomous driving, and vehicle connectivity. Therefore, industry professionals must stay current with technological advancements and proactively adapt to market shifts.

